This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Neurodivergent children are twice as likely to experience chronic disabling fatigue in adolescence
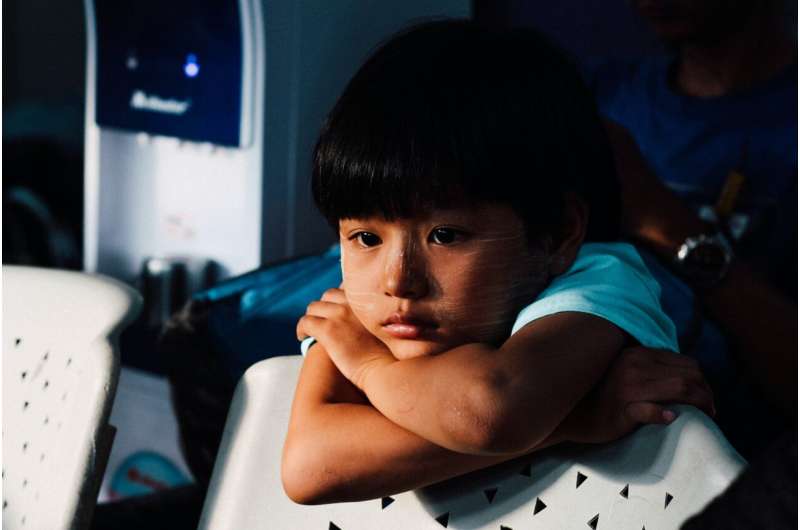

New research led by Dr. Lisa Quadt, Research Fellow in Psychiatry at BSMS and Dr. Jessica Eccles, Reader in Brain-Body Medicine at BSMS, highlights a significant link between neurodivergence and chronic fatigue. The study found that increased inflammation in childhood, often resulting from heightened stress levels, may be a contributing factor. This supports previous findings that suggest chronic fatigue can be rooted in inflammatory processes.
The work appears in BMJ Open.
"These results show the importance of trans-diagnostic screening for children and the need for better support for neurodivergent children," says Dr. Quadt. "Children with neurodivergent traits, diagnosed or not, often experience heightened stress, which is likely one reason for their increased inflammatory levels. Our study indicates that this may be a risk factor for developing chronic disabling fatigue, which dramatically decreases quality of life."
While this research emphasizes the higher risk of chronic fatigue among neurodivergent populations, it does not imply that all individuals with chronic fatigue are neurodivergent. The causes and mechanisms of chronic fatigue are multifaceted and intricate, necessitating a comprehensive approach by health care providers to identify contributing factors and tailor support and treatment accordingly.
The study's findings advocate for better screening practices and enhanced support systems for neurodivergent children to mitigate the risk of chronic fatigue and improve overall quality of life.
More information: Lisa Quadt et al, Childhood neurodivergent traits, inflammation and chronic disabling fatigue in adolescence: a longitudinal case–control study, BMJ Open (2024). DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-084203