This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies. Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
peer-reviewed publication
trusted source
proofread
Geographic approach to health finds risk of arthritis pain varies in communities
A University of Texas at Arlington researcher is taking an innovative look at a possible cause of chronic pain: where a patient lives.
"There is still very limited attention paid to the geography of pain—pain at the population level," said Feinuo Sun, assistant professor of kinesiology with expertise in demography and population health.
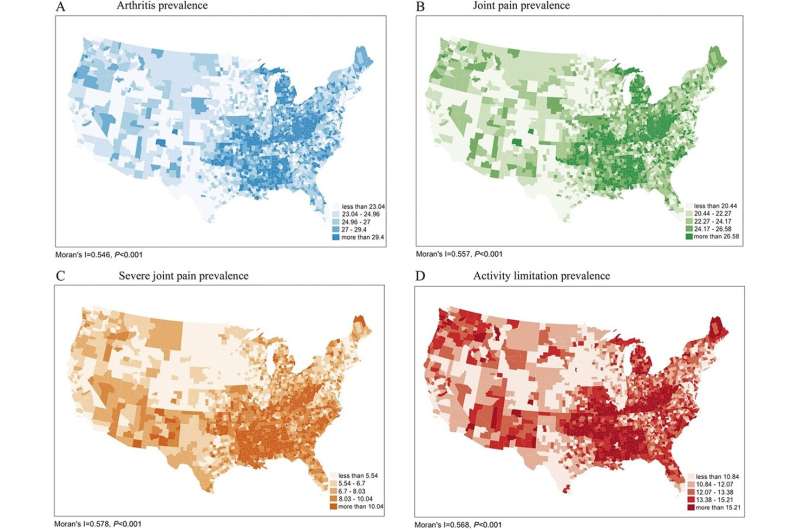
She recently completed research that found that the risk of pain varies among community members depending on where they live. Using national data sources and an innovative spatial analysis approach, Dr. Sun and her team took a deep dive to help further understand arthritis pain among Americans, tracking where it is most prevalent and why on the county level.
Their findings revealed that the Deep South, Appalachia and Michigan experience the most pain, while Texas, Arizona and the south Atlantic show high levels of spatial heterogeneity, meaning some but not all counties showed high prevalence of pain.
The report was published in Pain, It identifies possible reasons for such high levels of pain, including socioeconomic disadvantage, a lack of available treatment options like chiropractors and a lack of insurance. Sun and her co-authors also found the levels of severe pain to be especially high among racial/ethnic minority groups.
"Although they are not reporting joint pain or arthritis as often, they are more likely to develop more severe pain, with socioeconomic factors playing a role," Sun said.
That is where she says that more action is needed to help pain sufferers. The research team stresses that attention should be directed to counties with a concentration of disadvantaged populations, including minority groups and those facing family and economic distress.
"We need more localized policies at the state and county levels as well as more research so we can explore more recent trends and more fully understand causes of these geographic pain disparities."
More information: Feinuo Sun et al, The geography of arthritis-attributable pain outcomes: a county-level spatial analysis, Pain (2024). DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000003155